Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
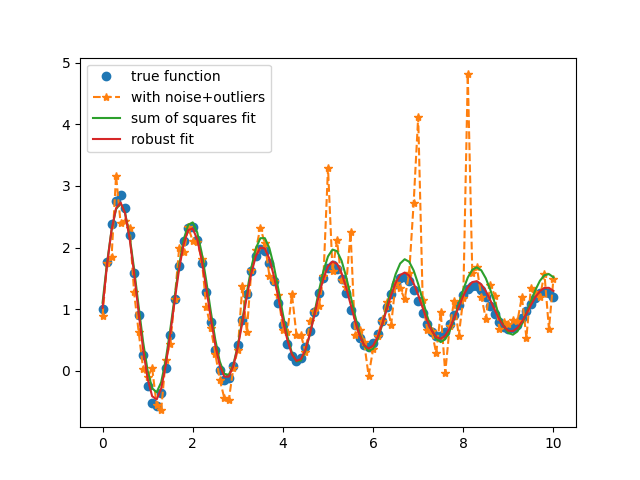
Fit Specifying Different Reduce Function¶
The reduce_fcn specifies how to convert a residual array to a scalar value
for the scalar minimizers. The default value is None (i.e., “sum of squares of
residual”) - alternatives are: negentropy, neglogcauchy, or a
user-specified callable. For more information please refer to:
https://lmfit.github.io/lmfit-py/fitting.html#using-the-minimizer-class
Here, we use as an example the Student’s t log-likelihood for robust fitting of data with outliers.
Generate synthetic data with noise/outliers and initialize fitting Parameters:
decay = 5
offset = 1.0
amp = 2.0
omega = 4.0
np.random.seed(2)
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 101)
y = offset + amp * np.sin(omega*x) * np.exp(-x/decay)
yn = y + np.random.normal(size=y.size, scale=0.250)
outliers = np.random.randint(int(len(x)/3.0), len(x), int(len(x)/12))
yn[outliers] += 5*np.random.random(len(outliers))
params = lmfit.create_params(offset=2.0, omega=3.3, amp=2.5,
decay=dict(value=1, min=0))
Perform fits using the L-BFGS-B method with different reduce_fcn:
# Fit using sum of squares:
[[Fit Statistics]]
# fitting method = L-BFGS-B
# function evals = 130
# data points = 101
# variables = 4
chi-square = 32.1674767
reduced chi-square = 0.33162347
Akaike info crit = -107.560626
Bayesian info crit = -97.1001440
[[Variables]]
offset: 1.10392444 +/- 0.05751441 (5.21%) (init = 2)
omega: 3.97313427 +/- 0.02073920 (0.52%) (init = 3.3)
amp: 1.69977037 +/- 0.21587469 (12.70%) (init = 2.5)
decay: 7.65901703 +/- 1.87209242 (24.44%) (init = 1)
[[Correlations]] (unreported correlations are < 0.100)
C(amp, decay) = -0.7733
# Robust Fit, using log-likelihood with Cauchy PDF:
[[Fit Statistics]]
# fitting method = L-BFGS-B
# function evals = 135
# data points = 101
# variables = 4
chi-square = 33.5081292
reduced chi-square = 0.34544463
Akaike info crit = -103.436577
Bayesian info crit = -92.9760949
[[Variables]]
offset: 1.02005970 +/- 0.06642640 (6.51%) (init = 2)
omega: 3.98224428 +/- 0.02898701 (0.73%) (init = 3.3)
amp: 1.83231341 +/- 0.27241877 (14.87%) (init = 2.5)
decay: 5.77328053 +/- 1.45140958 (25.14%) (init = 1)
[[Correlations]] (unreported correlations are < 0.100)
C(amp, decay) = -0.7584
C(offset, amp) = -0.1067
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.370 seconds)
